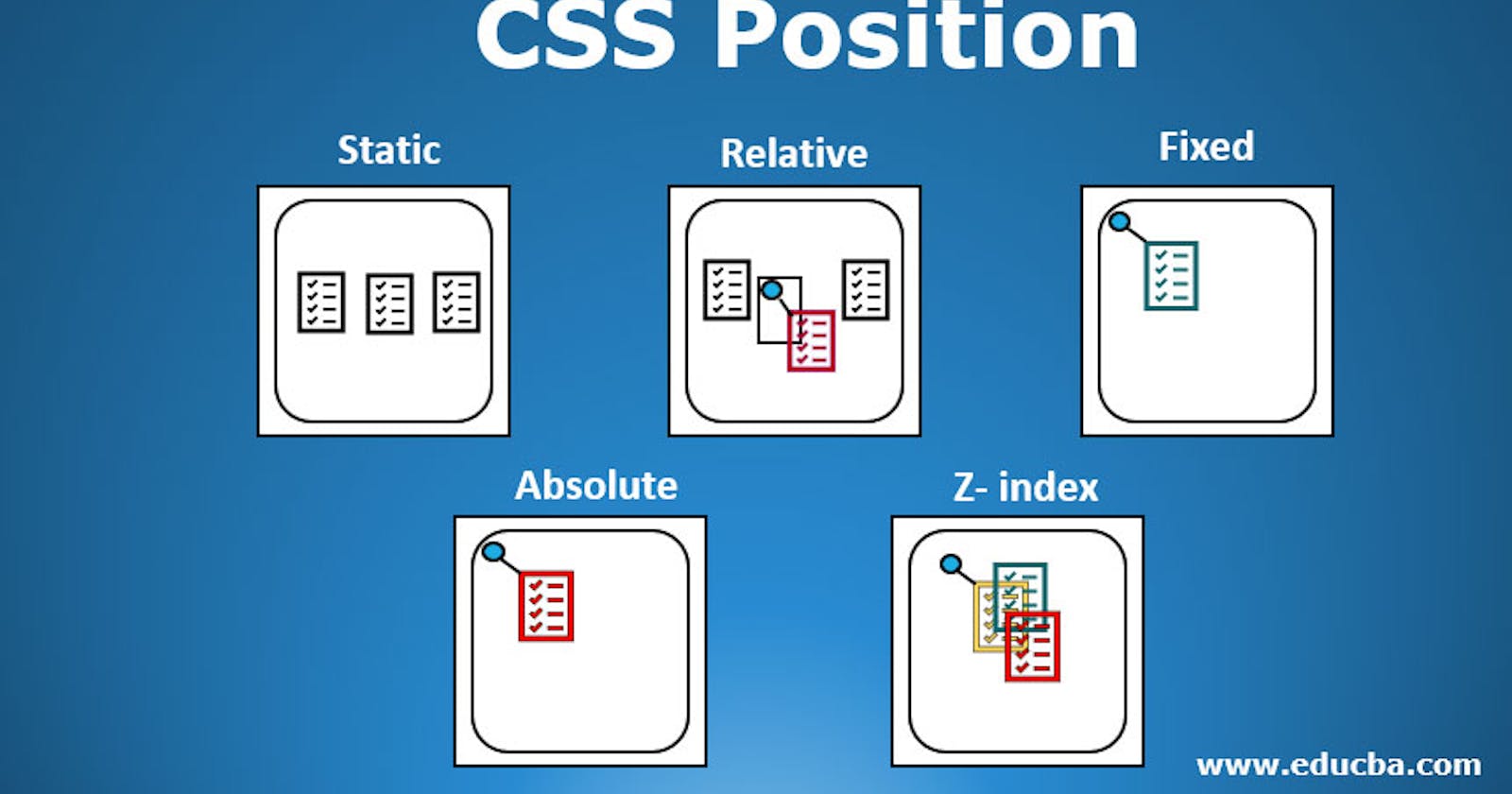
Position
The position CSS property sets how an element is positioned in a document. The top, right, bottom, and left properties determine the final location of positioned elements.
Syntax
position: static;
position: relative;
position: absolute;
position: fixed;
Static
The static position is the default positioning. The static element is positioned according to the normal flow of the document. The top,right, bottom , left .
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
div.static {
position: static;
border: 3px solid #73AD21;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2>position: static;</h2>
<p>An element with position: static; is not positioned in any special way; it is always positioned according to the normal flow of the page:</p>
<div class="static">
This div element has position: static;
</div>
</body>
</html>
Relative
An element with position: relative; is positioned relative to its normal position.
Setting the top, right, bottom, and left properties of a relatively-positioned element will cause it to be adjusted away from its normal position. Other content will not be adjusted to fit into any gap left by the element.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
div.relative {
position: relative;
left: 30px;
border: 3px solid #73AD21;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2>position: relative;</h2>
<p>An element with position: relative; is positioned relative to its normal position:</p>
<div class="relative">
This div element has position: relative;
</div>
</body>
</html>
Fixed
An element with position: fixed; is positioned relative to the viewport, which means it always stays in the same place even if the page is scrolled. The top, right, bottom, and left properties are used to position the element.
A fixed element does not leave a gap in the page where it would normally have been located.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
div.fixed {
position: fixed;
bottom: 0;
right: 0;
width: 300px;
border: 3px solid #73AD21;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2>position: fixed;</h2>
<p>An element with position: fixed; is positioned relative to the viewport, which means it always stays in the same place even if the page is scrolled:</p>
<div class="fixed">
This div element has position: fixed;
</div>
</body>
</html>
Absolute
An element with position: absolute; is positioned relative to the nearest positioned ancestor (instead of positioned relative to the viewport, like fixed).
However; if an absolute positioned element has no positioned ancestors, it uses the document body, and moves along with page scrolling.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
div.relative {
position: relative;
width: 400px;
height: 200px;
border: 3px solid #73AD21;
}
div.absolute {
position: absolute;
top: 80px;
right: 0;
width: 200px;
height: 100px;
border: 3px solid #73AD21;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2>position: absolute;</h2>
<p>An element with position: absolute; is positioned relative to the nearest positioned ancestor (instead of positioned relative to the viewport, like fixed):</p>
<div class="relative">This div element has position: relative;
<div class="absolute">This div element has position: absolute;</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>